On October 12th the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved a 2-dose schedule for Merck’s Gardasil-9® HPV vaccine for males and females ages 9-14.
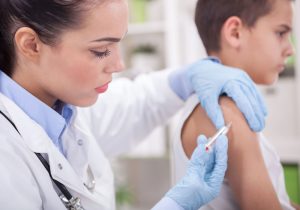 The new schedule calls for the second dose of the vaccine to be given 6-12 months following the first. The 3-dose schedule originally licensed with the vaccine may still be used, too; this regimen involves three doses administered over six months. Studies show the antibody response generated with the 2-dose regimen is not inferior to that observed with three doses.
The new schedule calls for the second dose of the vaccine to be given 6-12 months following the first. The 3-dose schedule originally licensed with the vaccine may still be used, too; this regimen involves three doses administered over six months. Studies show the antibody response generated with the 2-dose regimen is not inferior to that observed with three doses.
Following the FDA decision the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) updated its guidance and now routinely recommends the 2-dose regimen for all 11 and 12 year olds. CDC said reducing the number of shots and clinic visits makes it more convenient for parents to protect their children.
Gardasil® was introduced in the U.S. market in 2006 to prevent infections and diseases caused by two HPV types (HPV 16 and 18) found in a number of cancers, including most cervical cancers. Additionally, the vaccine protects against two low-risk HPV types (HPV 6 and 11) associated with most cases of genital warts. Gardasil 9® covers the HPV types included in the original vaccine and expands this protection by including five more “high-risk” HPV types (HPV 31, 33, 45, 52, and 58) that cause approximately 90% of cervical cancers globally along with a majority of vaginal, vulvar, and anal cancers.