
Fast Facts about HIV
HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Learn the basics about how HIV prevention, testing, and treatment.
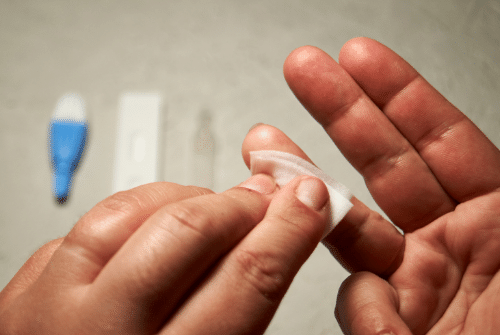
The only way to tell you have HIV is get tested. Testing is recommended at least once for everyone, and may be recommended more often for some. Testing can be quick, easy and confidential.
Knowing your HIV status has two important benefits. First, if you are HIV positive, you can take necessary steps before symptoms appear to get treatment, care and support services, potentially prolonging your life for many years. Second, if you know you are infected, you can take precautions to not pass on HIV to others.
If you have never been tested for HIV, you should be tested at least once. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends at least one HIV test for everyone aged 13 to 64 who visits a doctor. CDC also suggests being tested at least once a year if you do things that can transmit HIV infection. These include:
If you have been tested for HIV and the result is negative and you never do things that might transmit HIV infection, then you and your health care provider can decide whether you need to get tested again. Overall, you should talk to your provider about how often to get tested for HIV.
The most common HIV tests look for antibodies to the virus. CDC states that most people infected with HIV will have detectable antibodies within 3 months of exposure to HIV, the average being 25 days. Rarely, it can take up to six months.
Testing early has many benefits. People who know whether they are infected or not can take precautions to protect themselves and others in future. HIV-infected individuals can benefit from early treatment.
There are many places to get HIV testing, including local health departments, private doctors, hospitals and sites set up specifically to test for HIV. It is important find a testing site that offers HIV counseling as well as the test. HIV counselors can provide you with important information about the test, discuss your risks for HIV, answer your questions about your risk for HIV and how to protect yourself and others in the future. They also can provide information about other resources available in the area.
Some locations may have rapid tests that can tell if you are infected within 30 minutes, while in other locations it may take up to 2 weeks to get results. Check with the test site to find out what type of HIV tests they have.
There are home collection kits that allow you to take your own blood sample and send it in to be anonymously tested. The only test approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for home collection is OraQuick. You can purchase this test in most drug stores, but it is also available for purchase online.
No. The test for HIV can only tell you if you have been infected or not. Transmission of the virus does not necessarily occur every time exposure occurs. The only way for an individual to tell if they have been infected with HIV is to be tested. If you are unsure of your partner’s status, you may want to consider talking to them about it and using protection to reduce your risk.
There are many things you can do to help protect your health if you test positive for HIV. Seeking health care early and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help a person stay healthy. Some specific things you can do if you’re positive for HIV are:
The CDC (1-800-CDC-INFO) can provide you with more information what to do if you test positive for HIV. They can also provide you with referrals to health care providers, treatment programs and other services for HIV-infected individuals.
There are specific places that you can get tested for HIV. It is recommended that you get the HIV test done at a health clinic, at a lab or at an HIV/AIDS voluntary counseling and testing (VCT) site. When you attend to get tested, you will see a doctor, trained counselor, a nurse or some other health professional in private. He or she will explain what the test involves and what the result means.
Counseling should be made available to all people getting HIV tests. If it is not, it can be requested. Counseling is important to help people deal with the results of their test, to discuss ways to keep themselves healthy, and to make them aware of the resources in their community.

HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Learn the basics about how HIV prevention, testing, and treatment.

HIV and Pregnancy There is a lot to think about when you want to have a baby or when a baby is on the way. One important step is to
Living with HIV If you have been diagnosed with HIV, seeking health care early and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help a person stay healthy. There are many new drugs

September 27 is National Gay Men’s HIV/AIDS Awareness Day. This national awareness day was first launch in 2008 by the National Association of People with AIDS (NAPWA), as a way

World AIDS Day takes place each year on December 1st. The annual observation is held to bring attention to the global impact of HIV/AIDS. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention

PrEP PrEP stands for pre-exposure prophylaxis. The word prophylaxis means to prevent or control the spread of an infection or disease. The goal of PrEP is to prevent HIV infection
ASHA believes that all people have the right to the information and services that will help them to have optimum sexual health. We envision a time when stigma is no longer associated with sexual health and our nation is united in its belief that sexuality is a normal, healthy, and positive aspect of human life.
ABOUT
GET INVOLVED
ASHA WEBSITES
GET HELP
© 2024 American Sexual Health Association