New Recommendations to Make IUD Insertion Less Painful
There is new guidance on pain management for IUD insertion and acknowledgement that providers often underestimate the pain patients feel during their procedures.
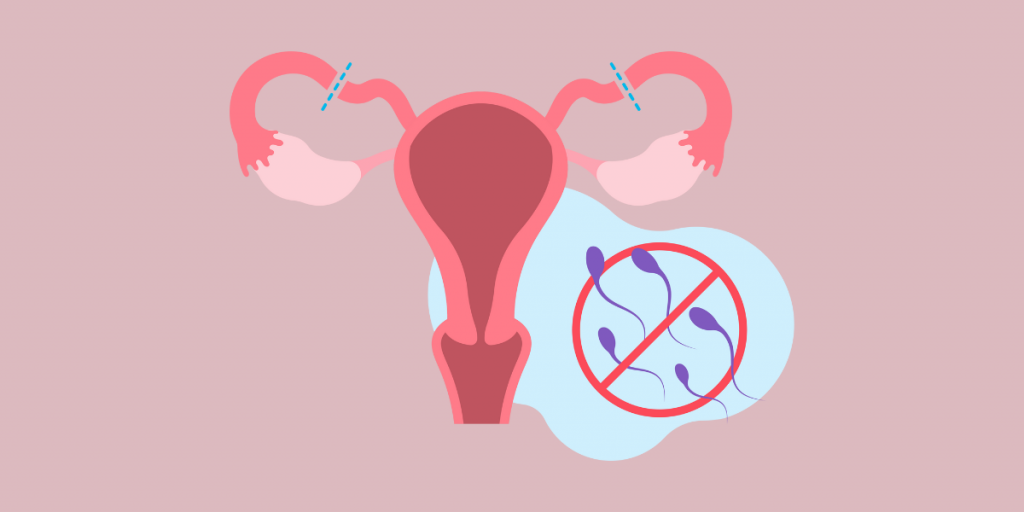
A new study says we might be overestimating just how good tubal ligation is at preventing pregnancy. In fact, the study suggests that “getting your tubes tied” may be less effective than the contraceptive implant or even the IUD.
When eggs are released during ovulation, they travel down the fallopian tubes toward the uterus. If sperm and egg meet, fertilization happens in the fallopian tube. Then the fertilized egg travels the rest of the way down the tube to the uterus.
Tubal ligation cuts, clips, or removes the fallopian tubes to prevent sperm and egg from ever meeting. This procedure is permanent and cannot be reversed.
Tubal ligation has always been thought of as the most effective form of birth control because it is a structural change to the reproductive anatomy. This new study, however, suggests it may be less effective that we’ve thought.
The study’s authors looked at data from the National Survey of Family Growth (NSFG) collected at intervals between 2002 and 2015. (There are newer editions of the NSFG, but they weren’t included because some of the data needed for these analyses were not made public for those years.)
The NSFG asks couples to recall their contraceptive use over a period of time and then asks whether they experienced a pregnancy during that time. This data is used to calculate the effectiveness of many contraceptive methods. For this analysis, the authors looked at people who answered “yes” to the question “Have you ever had both of your tubes tied, cut, or removed? This procedure is often called a tubal ligation or tubal sterilization.”
In the 2013 to 2015 wave of the survey, the analyses found that an estimated 2.9% of women who underwent a tubal sterilization procedure got pregnant within the first 12 months after the procedure. Even more (8.4% percent) got pregnant within 10 years. The 12-month estimated rate of pregnancy was higher for women under 25 (3.9%) and those 26-34 (3.3%). There were no pregnancies among tube-tied women over 35.
In contrast, fewer than 1% of users of contraceptive implants or IUDs get pregnant within the first year of use and this stays the same for the life of the device. The implant lasts three years while IUDs last anywhere between three and ten years.
The study can’t answer the mechanics of how pregnancy is happening post-procedure. The lead author theorized that there may be microscopic gaps where the tube is tied off or clipped that are big enough to allow sperm to get through to an egg. In order for a person to become pregnant, those gaps would also have to be big enough to let a fertilized egg travel down to the uterus.
The study also can’t answer which method of tubal ligation results in the most effectiveness because the NSFG did not ask participants what method their doctor used. Some experts are advocating for doctors to remove fallopian tubes entirely instead of tying or clamping them. This not only helps prevent pregnancy but might also protect women from ovarian cancer which often starts in the fallopian tubes. The authors of this study agree that removing both tubes is likely more effective than older surgical methods but say that we don’t have the data to prove that yet.
We need more research on the effectiveness rates of surgical sterilization. In the meantime, anyone who is considering which contraceptive method will be best for them should keep this study in mind. Long-acting reversible contraception (LARC) options like the implant or IUD are excellent alternatives to sterilization. They are 99% effective in preventing pregnancy and require very little effort on the part of the user. Once they are inserted by a health care provider, they prevent pregnancy for between three and ten years. And unlike surgical sterilization, these methods are removable if someone changes their mind about pregnancy.

There is new guidance on pain management for IUD insertion and acknowledgement that providers often underestimate the pain patients feel during their procedures.
Our reproductive health is an important part of our sexual health and our overall health. It includes our reproductive organs and our ability to get pregnant or get someone pregnant when we choose.

Anyone who is having penis-in-vagina sex runs the risk of getting pregnant every time they have sex. Even if it’s your first time. Even if you have your period. Even if it’s a full moon and Mercury is in retrograde.

LARC methods are safe, reliable, and prevent pregnancy for years. For many people they are a great choice, but everyone has personal preferences for what fits in to their lifestyle and health profile.

Infertility can stem from factors affecting both men and women. Sometimes, these are related to sexually transmitted infections.
The Biden Administration proposed new rules designed to make getting contraception easier and less expensive.
Public health experts have said that every case of congenital syphilis is a failure of STI screening and prenatal care. A new study looked more closely at cases to see what factors in a pregnant person’s life were most associated with congenital syphilis.
Women in states with restrictive abortion laws have few options today. And yet the prescriptions for birth control methods has fallen since the Dobbs decision.
ASHA believes that all people have the right to the information and services that will help them to have optimum sexual health. We envision a time when stigma is no longer associated with sexual health and our nation is united in its belief that sexuality is a normal, healthy, and positive aspect of human life.
ABOUT
GET INVOLVED
ASHA WEBSITES
GET HELP
© 2025 American Sexual Health Association