It has been associated with urethritis in men and linked to cervicitis and pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women. In one study of young men and women, it was found to be more common than gonorrhea infection. But odds are you’ve never been tested for, or even heard of, this sexually transmitted bacterial infection.
So what is it?
Mycoplasma genitalium, or Mgen, was first identified in 1981. It is a bacterium that can infect the reproductive tract and is passed on through sexual contact. In men, infection with Mgen can cause urethritis (swelling and irritation of the urethra), and in women it has been linked to cervicitis (inflammation of the cervix), PID, and possibly infertility.
How common is it?
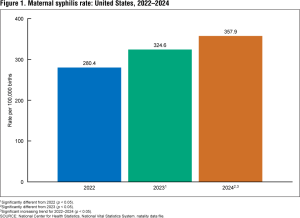
While there aren’t statistics to show how common infection with Mgen is, in one study of 2,932 young men and women, Mgen was more prevalent that gonorrhea, but less than chlamydia and trichomoniasis. Like those infections, Mgen can be asymptomatic, particularly in women. Women may have pain with urination, vaginal discharge, or discomfort with sex, while men may experience burning, painful urination and sometimes a discharge from the penis.
How do you test for it?
There are currently two FDA-approved diagnostic tests for Mgen. Labs can use a specific type of test method—nucleic acid amplification testing (NAAT)—to identify an Mgen infection. Testing can be done on urine, cervical swabs, or urethral swabs.
Can it be treated?
Since Mgen is a bacterial infection, it can typically be cured with antibiotics, sometimes with a single dose. Occasionally, if a first course of antibiotics doesn’t cure the infection, an additional antibiotic treatment may be required.